Theory of Constraints (TOC), also known as Bottleneck theory, was developed by Israeli physicist and entrepreneur Eliyahu M. Goldratt. This theory is a management approach that aims to improve organizational performance by focusing on identifying and eliminating bottlenecks.
A bottleneck is a part of the production process or a resource that limits a company's production capacity and thus affects overall performance. Similar to a bottleneck that reduces the flow of a liquid, creating a bottleneck, certain factors in organizations create bottlenecks that can slow, limit or prevent operations.
Back to overview
Theory of Constraints
Table of contents
1. Basic Principles Of The Theory Of Constraints
Bottleneck theory is based on several fundamental principles:
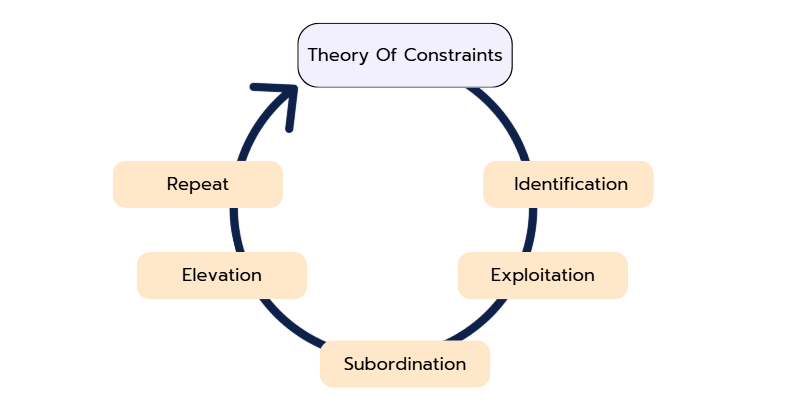
- The flow principle:
TOC emphasizes that a company's production should be designed to function like a continuous flow. Each step in the process should be matched to the speed of the bottleneck to avoid congestion and overproduction. - Identification of the bottleneck:
Identification of the bottleneck is critical. This step requires a detailed analysis to identify the resource or process step that has the highest capacity constraint. - Exploitation (utilization of the bottleneck):
After identifying the bottleneck, the company should ensure that it is optimally utilized. This means that all resources and activities should be directed towards using the bottleneck as efficiently as possible. - Subordination:
All other activities in the organization should be subordinate to the performance of the bottleneck. This means that the speed and output of the bottleneck determines the speed and output of the entire process. - Elevation (Elevating the Bottleneck):
If the bottleneck can be permanently eliminated or its capacity can be increased, the elimination should also be considered to increase the overall performance of the company. To this end, it may also be profitable to invest costs to remove the bottleneck, which will subsequently be recouped through an improved process and improve production operations.
2. Examples From The Economy
- Manufacturing companies:
In the manufacturing industry, bottleneck theory is particularly relevant. A classic example is the production of cars. If the assembly line is faster than the supply of engines, production will be limited by the availability of engines, leading to inefficient labor processes and inventory. TOC would suggest optimizing the bottleneck, engine supply, and ensuring that it is synchronized with the assembly line.
=> Check out some of our Car-Cases to learn for your upcoming case interview:
Bain + BCG - Hot Wheels WITH VIDEO SOLUTION
Problem definition: Our client is Korean Car Parts (KCP), a multi-national original equipment manufacturer (OEM) of car parts based in Korea. They've recently seen a decline in profits and have brought us in to understand how to address this falling profitability.========================================================To get a deep-dive explanation of the case leadership behind this case, please read this article: Candidate-Led Cases: What to Expect With Example CasesThis case is part one of a series. The goal of this series is to demonstrate how an identical case prompt (and corresponding framework) could lead to multiple different outcomes. The goal is to train you to adjust to case information in an agile and adaptable way.The 2nd part of the series can be found here:Case - BCG Hot Wheels Part 2 With Video Solution
Competitive response
Growth strategy
Market analysis
Operations strategy
Profitability analysis
Pickup Manufacturer
The automobile manufacturer CarsCo has difficulties with the profitability of its pick-up unit in Thailand. The candidate is supposed to evaluate the situation by answering a line of questions that are presented in the “suggested approach” section.
Market analysis
Profitability analysis
Bain + BCG Hot Wheels - Part 2 WITH VIDEO SOLUTION
Our client is Korean Car Parts (KCP), a multi-national original equipment manufacturer (OEM) of car parts based in Korea. They've recently seen a decline in profits and have brought us in to understand how to address this falling profitability.=================================================To get a deep-dive explanation of the case leadership behind this case, please read this article: Candidate-Led Cases: What to Expect With Example CasesThis case is part two of a series. The goal of this series is to demonstrate how an identical case prompt (and corresponding framework) could lead to multiple different outcomes. The goal is to train you to adjust to case information in an agile and adaptable way.The 1st part of the series can be found here: Case - BCG Hot Wheels With Video Solution
Market analysis
Profitability analysis
- Service companies:
The bottleneck theory is also applicable in service companies. For example, a call center may have bottlenecks in the number of available customer service agents*. If calls come in faster than they can be handled, this leads to long waiting times and dissatisfied customers. TOC would suggest here to optimize the work capacity of the customer service team to eliminate the bottleneck. - Scientific findings and studies:
There are numerous scientific studies and case studies that demonstrate the effectiveness of bottleneck theory in practice. A study by R. H. Lenz and S. L. Nydick in 1991, for example, found that companies that implemented TOC experienced significant improvements in lead times, inventories, and profits. This underlines the scientific validity of this management method. - Bottleneck theory in management consulting:
In management consulting, bottleneck theory is often applied to help companies identify and eliminate bottlenecks. Consultants* analyze internal processes, identify bottlenecks, and then develop strategies for optimization. TOC provides clear guidance for improving operational efficiency and performance.
In summary, Eliyahu M. Goldratt's bottleneck theory is a proven approach to improving business performance that has been successfully applied in a variety of industries. Scientific research supports its effectiveness, and in management consulting it plays an important role in optimizing operations and maximizing profits.
Let's Move On With the Next Articles:
Income Statement
Common Terms of Business
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement (P&L), provides a summary of a company's annual revenues, costs, and profits/losses. It is one of the three key financial documents, alongside the balance sheet and cash flow statement.The income statement records revenues and expenses at the time they are incurred (accrual accounting). For example, an invoice appears in a company's income statement on the day it is generated, regardless of when the payment is made. In contrast, in the cash flow statement, an expense is recorded only when the payment is actually made.Example:Suppose a company sells products worth €100,000 and receives a bill for material costs of €40,000. In the income statement, the revenue of €100,000 is recorded at the time of the sale, and the material costs of €40,000 appear simultaneously.
Herzbergs 2-Factor Theory
Common Terms of Business
The Herzberg 2-factor-theory, also known as the two-factor theory or motivation-hygiene theory, was developed in the 1950s by Frederick Herzberg. Herzberg was an American industrial scientist and psychologist who taught as a professor at various universities. His research interests focused on what makes people satisfied at work.His theory aims at explaining and influencing motivation and satisfaction at work. It postulates that there are two distinct groups of factors that influence job satisfaction and dissatisfaction, and they have different effects on employees.Herzberg's research findings are also more relevant than ever in today's work environment, especially in light of the shortage of skilled workers, burnout, and in the debate about a 4-day work week.
Cash Flow Statement
Common Terms of Business
The cash flow statement is one of the three primary components of a company's financial report, alongside the balance sheet and the income statement. It provides detailed insights into a company's cash movements and tracks how liquid assets change over a specific period. Unlike the income statement, which records revenues and expenses as they are accounted, the cash flow statement only includes actual cash transactions. This clarity allows businesses to understand how much cash they are truly earning and spending, offering vital information about liquidity and financial stability. The Three Main Categories of Cash FlowCash flows are classified into three main categories: operating cash flow, investing cash flow, and financing cash flow. Each category provides insights into different financial aspects of a business and collectively paints a picture of its liquidity.Operating Cash Flow (CFO): Operating cash flow represents cash generated from a company’s core activities—producing and selling goods or services. It reveals whether the day-to-day operations generate enough funds to sustain the business.Investing Cash Flow (CFI): Investing cash flow reflects long-term investments, such as purchasing property, equipment, or other assets. This metric shows how much money the company is allocating to drive future growth or improve productivity.Financing Cash Flow (CFF): Financing cash flow includes activities related to funding the business, such as issuing or buying back bonds and stocks or paying dividends. It illustrates how the company raises capital or returns value to its shareholders. How are Cash Flow, Income Statement, and Balance Sheet Interrelated?Cash flow, the income statement, and the balance sheet are closely interconnected and influence each other.Deriving Operating Cash Flow from the Income StatementOperating cash flow is derived from the income statement, using the EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) as the starting point. Specific adjustments are made to determine the actual cash flow generated from operating activities.First, non-cash expenses, such as depreciations, are considered. Depreciations reduce accounting profit but do not result in a real cash outflow, so they are added back to the EBIT.Additionally, cash-related items outside the EBIT are included. A typical example is taxes paid: although taxes are not part of the EBIT, they represent a real cash outflow and are therefore subtracted.Changes in working capital (net working capital) can also impact the operating cash flow. These include increases or decreases in inventory, receivables, or payables, which affect actual cash flows.These adjustments ensure that the operating cash flow reflects the liquid funds genuinely generated or used by the company's operating activities.The Balance Sheet as a Basis for Investment and Financing Cash FlowsTo calculate investment and financing cash flows, the balance sheets of the past two years are used.Investment Cash Flow: This can be observed on the asset side of the balance sheet. An increase in assets due to investments indicates cash outflows, while a decrease, such as reducing inventory, reflects cash inflows.Financing Cash Flow: This is derived from the liabilities side of the balance sheet. An increase in equity or liabilities suggests that the company received additional funds, such as through loans or issuing new shares.Ultimately, all three types of cash flows—operating, investment, and financing cash flows—culminate in a net change in the company’s cash position. This change is reflected in the balance sheet as the difference in cash balances between two fiscal years.In the next section, you’ll see an example of how the three types of cash flows can be calculated indirectly. Example: Indirect Calculation of the Three Cash Flow Types PositionAmount(Operating Income) EBIT$100,000Income Taxes Paid-$20,000Depreciation and Amortization$50,000Change in Inventory-$40,000Change in Accounts Receivable$10,000Change in Accounts Payable$20,000= Cash Flow from Operating Activities (CFO) $120,000 Purchase of Intangible Assets-$20,000Change in Property, Plant, and Equipment-$300,000Sale of Business Units$100,000= Cash Flow from Investing Activities (CFI) -$220,000 Dividends Paid-$20,000Interest Paid-$30,000Change in Long-Term Liabilities$130,000= Cash Flow from Financing Activities (CFF) $80,000 Net Change in Cash (CFO + CFI + CFF)-$20,000 This table illustrates how the three types of cash flows contribute to changes in cash. Although the company generated $120,000 from operations, significant investments (-$220,000) outweighed the inflows. Additional financing (+$80,000) reduced the cash decline to -$20,000. Cash Flows and Their Role in Valuing a CompanyCash flows play a crucial role in determining a company’s value, especially when it comes to "free cash flow". Free cash flow shows how much money a company has available to distribute to shareholders as dividends or interest payments without using funds needed for day-to-day operations. For investors, this is an essential metric as it reveals how profitable and financially stable a company truly is.A company’s value is often calculated based on its free cash flow using a method called "Discounted Cash Flow" (DCF). This involves estimating future cash flows and discounting them to their present value to determine how much the company is worth today.To calculate free cash flow, non-cash expenses like depreciations, which don’t represent actual cash outflows, are added back to the income statement figures. After that, all necessary investments required to keep the business running, such as working capital, short-term receivables and payables, and capital expenditures for things like equipment or real estate, are subtracted.The final figure provides a clear picture of the company’s potential to generate value and make payments to shareholders. Below is an example calculation to illustrate this. PositionAmount(Operating Income) EBIT$100,000Income Taxes Paid-$20,000Depreciation and Amortization$50,000Working Capital Changes-$10,000Investments (Intangible + Equipment)-$280,000= Free Cash Flow-$160,000 Practical Applications of Cash Flow Analysis in Case InterviewsA cash flow analysis is a common tool in case interviews to evaluate a company's financial health and guide strategic decisions. Candidates are expected to interpret different cash flow categories and derive practical recommendations. Below are four typical scenarios where the cash flow analysis can play a key role in case interviews:Assessing a Company's Financial StabilityA company must ensure it has enough funds to meet its short-term obligations. By analyzing the operating cash flow, you can determine if the business can sustain itself financially. A positive operating cash flow is a strong indicator of stability and short-term liquidity. Deciding on Investments in New ProjectsWhen evaluating a significant investment, such as building a new production facility, the free cash flow becomes a critical metric. It helps determine whether the company can finance the project without jeopardizing its liquidity. A sufficient free cash flow indicates that the business has the resources to support growth initiatives. Valuing an Acquisition or MergerIf a client is considering acquiring a company, a cash flow analysis can help estimate the target company's future value. The Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method is a common valuation approach used to assess whether the acquisition price is justified and how the transaction might impact the cash flow. Analyzing Cash Conversion Efficiency for a Manufacturing BusinessFor a manufacturing company struggling to generate cash quickly, the Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC) is a key metric. A short CCC reflects operational efficiency and the ability to convert resources into cash quickly. A long CCC, however, highlights inefficiencies and areas for improvement. Key TakeawaysCash flows are crucial for assessing liquidity. A positive cash flow indicates at least short-term solvency.Cash flow comes from three main sources: operations, investments, and financing activities.Operating cash flow helps evaluate a company’s ability to sustain its daily operations.Investment cash flow provides insights into opportunities for future growth through investments.Financing cash flow shows how a company raises capital or returns it to shareholders, serving as a marker of financial strategy and capital structure.Practical use in case interviews: A cash flow analysis helps assess financial stability, investment potential, acquisition decisions, and the efficiency of working capital management.
