Pareto's 80-20 principle is a general rule of thumb that describes an unequal distribution between causes and effects. The principle states that 80% of overall results are driven by 20% of inputs. For example: 80% of work requires 20% effort, 80% of a project requires 20% of the time, and 80% of revenue comes from 20% of clients. When analyzing case problems, the Pareto rule can be utilized to diagnose big issues that might be caused by a much smaller problem. On the other hand, problems that seemingly look huge might result in only a small issue.
Pareto Principle
Use the Pareto Principle to Logically Focus on Critical High-Impact Areas
The Pareto Principle highlights a common approach for consultants: solving a problem where you can produce the highest positive impact with the lowest amount of effort because consultants usually have very limited time to work on a problem. During a McKinsey, BCG, or Bain interview, you need to find a solution in less than an hour. Therefore, focusing on important aspects of the case is crucial.
Apply the Pareto Principle in Case Interviews
The Pareto Principle should be intuitive when evaluating options to determine the root causes of problems and their solutions. For instance, look at the chart below, the costs per sold product from an analysis of an online store:
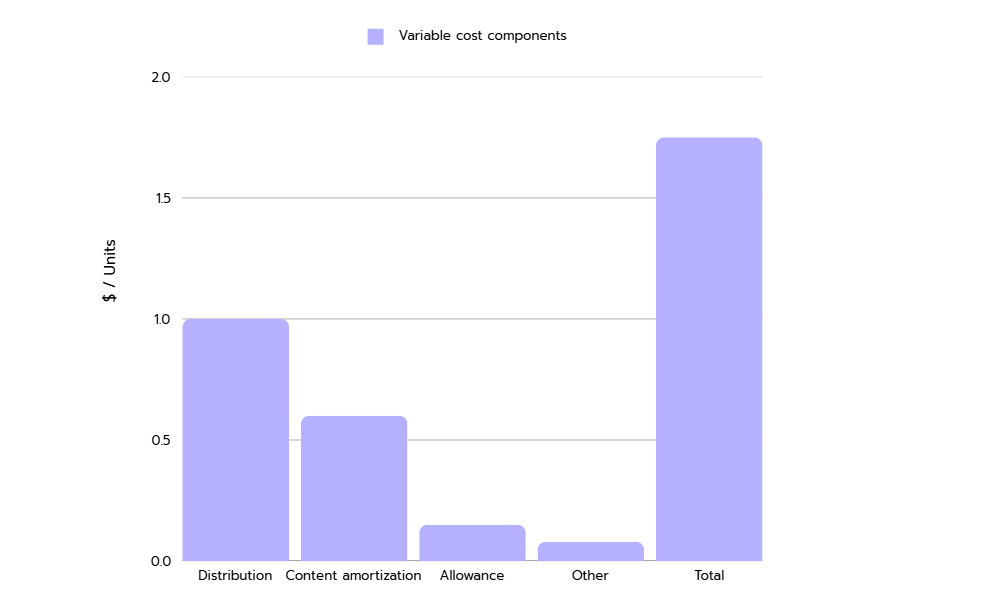
If you want to reduce the total costs by 10%, you need to save 17.5 cents. By a thorough breakdown of costs, you can focus on the ones with the highest impact: distribution and amortization costs.
Reducing only distribution and amortization costs by 10% will yield savings of 16 cents.
Impact Analysis:
- Changing 50% of costs positions (distribution and amortization) leads to 91% (16/17.5) of planned cost reduction.
- In other words, only 50% of the possible effort is required (assuming reduction of costs by 10% requires the same effort for every cost position).