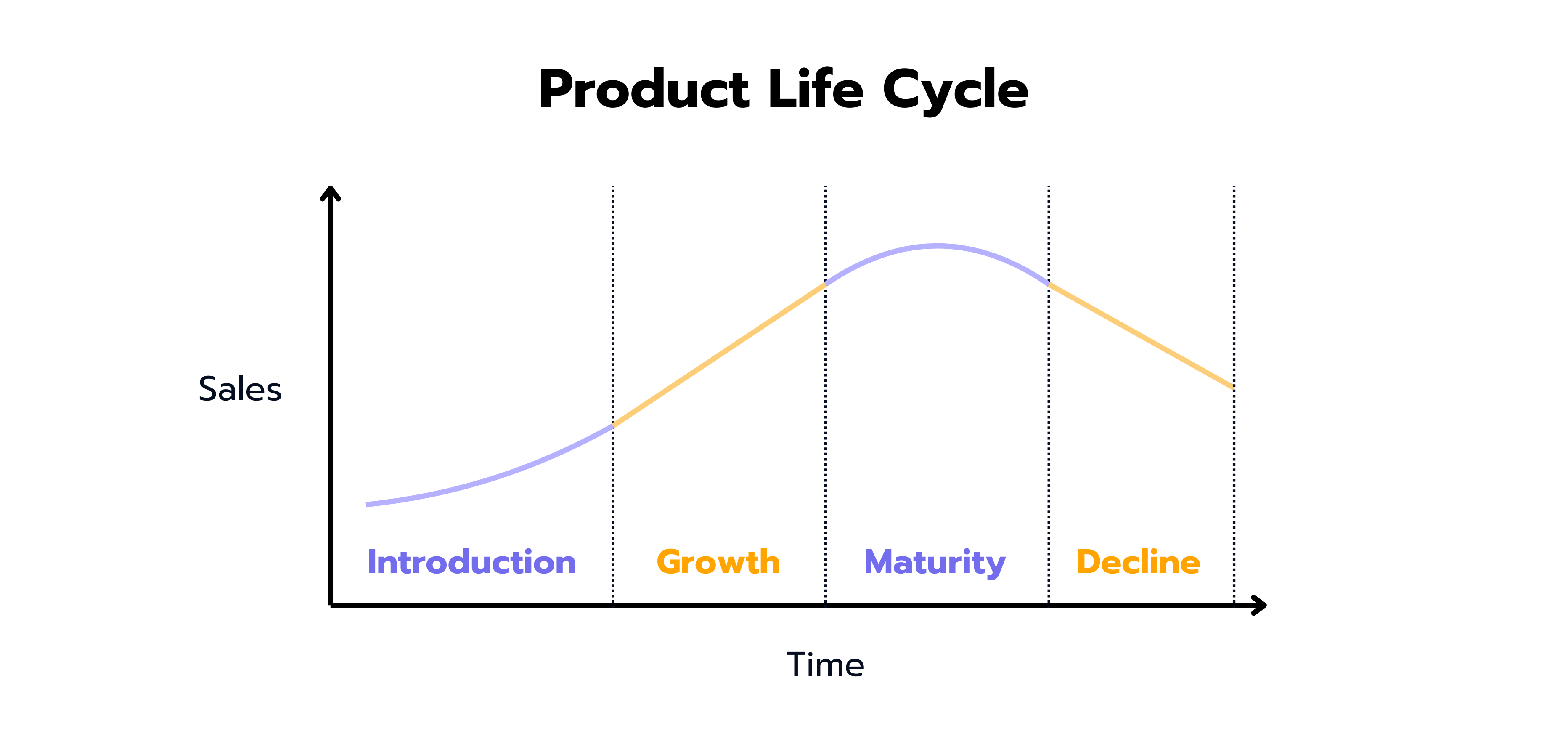
The product life cycle is a way to map the common stages a product undergoes throughout its lifespan. The product life cycle is typically divided into 5 different stages, each having specific strategic decisions affecting profits and revenues.
Product Life Cycle
Four Stages of the Product-Life-Cycle
(1) Development: In the development phase, the product has just been finished and the most important facts and figures have been determined. As no profits are made here, this phase is not shown in the curve diagram.
(2) Introduction: In the first phase, the product is introduced. Normally, at this stage, there are a few competitors and customers. Therefore, sales and profit are low and the risk that the product will not succeed is high. In order to boost sales, the focus lies heavily on promotion activities.
(3) Growth: Products that succeed in addressing customer’s needs will lead to an increase in sales. Advertisement is still a key component to promote further growth.
(4) Maturity: At this stage, the product can be seen as well established and widely accepted within the targeted customer group. Profits are high and risks are low. Typically, in this phase, competition increases. To keep the market position and expand this phase, companies often employ strategies such as the introduction of complementary or updated products or simply invest in marketing activities.
(5) Decline: At this point, the product may not fulfill the current needs of the customers, and sales start to decline. The important decision at this stage is deciding when to take the product off market, such that the client optimizes financial gains and minimizes losses due to time and investment.
Meaning of the Product-Life-Cycle in Case Interviews
The product life cycle is a key concept in case interviews, especially when dealing with market entry, competitive strategy, or growth opportunities. Candidates should be familiar with the different stages and be able to derive strategic decisions accordingly.
A common case question might be: "A company is planning to launch a new product. What factors should be analyzed to maximize success in the introduction phase?" A structured approach should consider aspects such as market demand, competitive landscape, pricing strategy, and marketing efforts. Similarly, cases related to the maturity or decline phase could focus on whether a product should be further developed or phased out.
Solve Cases to Topics Like Market Entry or New Product
Key Takeaways About the Product-Life-Cycle
- The product life cycle describes the 5 phases a product goes through.
- These phases can be divided into Development, Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline.
- Each phase has an impact on profit, sales, and the company’s strategic decisions.