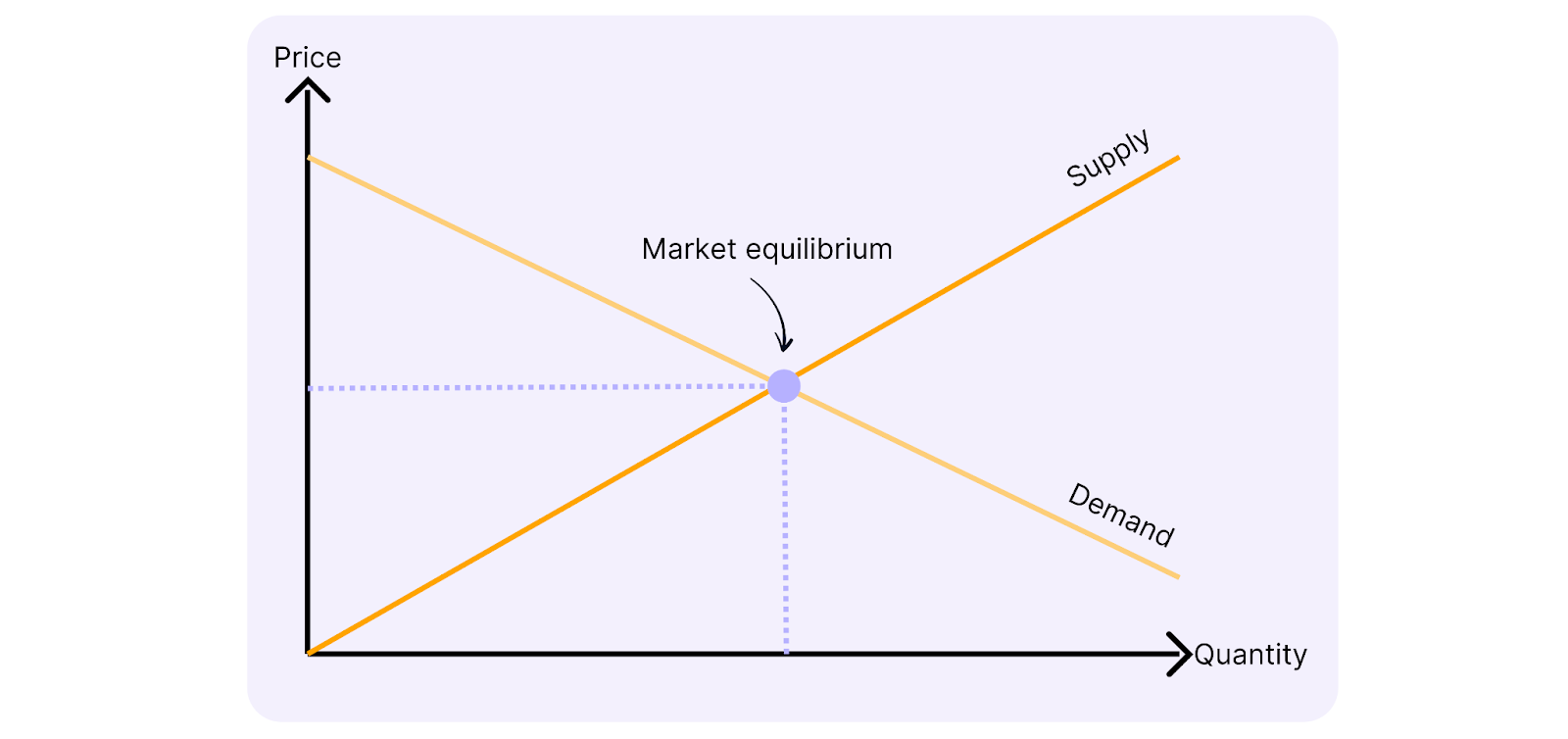
Supply and demand are economic concepts that directly influence pricing and competition. The law of supply and demand states that the availability of a product (supply) and the desire for it (demand) determine its price. When demand is high and supply is low, prices rise – and vice versa. This knowledge is not only theoretically important, but also plays a crucial role in consulting projects, particularly when developing market strategies.
Let’s take a closer look at supply and demand in case interviews! ✨