When preparing for case interviews, you'll quickly find that "fixed costs" and "variable costs" always come up. These concepts are important not only for financial analysis but also for strategic decision-making in companies. Let’s explore what these costs are and how you can skillfully use them in your cases. ✨
Fixed & Variable Costs
What are Fixed and Variable Costs?
Fixed Costs are expenses a company incurs regularly, regardless of how much it produces or sells. These costs stay constant whether the company is active or not. Typical fixed costs include:
- Rent
- Salaries for full-time employees
- Administrative expenses
- Depreciation
Whether a company sells a lot or just a little, these fixed costs still need to be covered. They form the basis of a company’s cost structure and are crucial for long-term planning.
Variable Costs, however, directly depend on business activity and change with the production level. They increase as more is produced and decrease when production is reduced. Examples of variable costs include:
- Raw materials
- Energy costs
- Wages for temporary staff
An important point is that variable costs ideally drop to zero when there is no production. This makes them particularly flexible, as they can adapt to the current business situation.
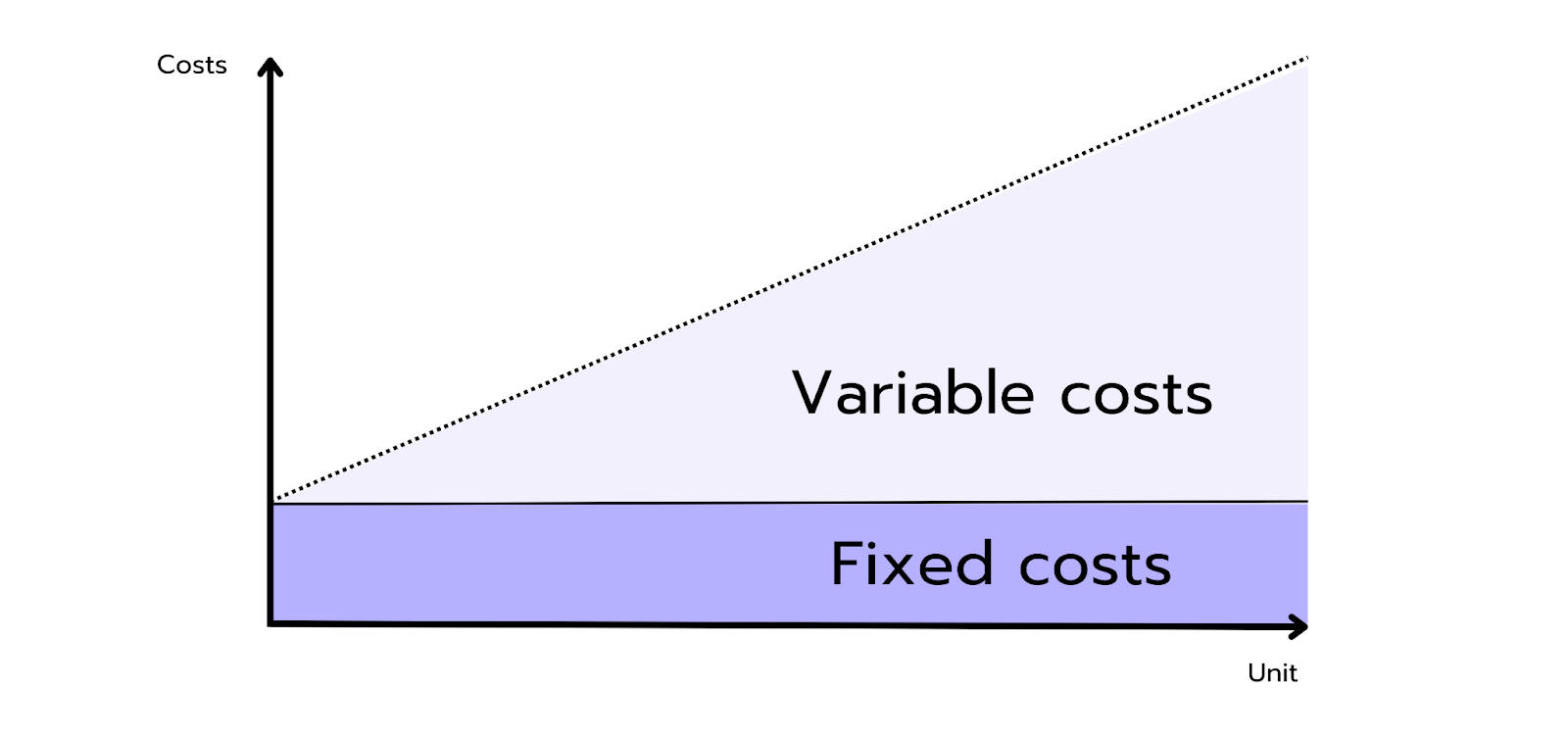
Together, these two cost types – fixed and variable costs – form a company’s total costs. To get a complete picture of the company's financial position, it’s crucial to divide costs into these two categories.
At this point, be sure to check out the profitability framework. Profit is calculated by subtracting total costs from revenue. To understand cost behavior, it’s essential to segment them into fixed and variable costs – a perfect exercise!
You can find more frameworks in our Case Interview Basics. 🚀
Applying Fixed and Variable Costs in Case Interviews
In case interviews, you’ll often need to analyze a company's financial aspects. A strong understanding of fixed and variable costs is essential, as it helps you make strategic decisions and offer precise recommendations. Here are some points to consider during case analysis:
- How do fixed costs impact the company's profitability?
Fixed costs place a burden on companies, especially during uncertain times. Analyzing the ratio of fixed costs to revenue is important to identify cost-cutting measures. Companies with high fixed costs rely on stable sales to remain profitable. - How do increasing variable costs affect the profit margin?
Rising variable costs, like raw material prices, can reduce profit margins and may require price adjustments. This impacts competitiveness, so competitor reactions should also be considered. - Are there ways to reduce variable costs to improve overall profitability?
The company can optimize variable costs through more efficient production methods or better supplier terms. Innovative cost-saving approaches can boost profitability. - How does a change in production volume affect total costs?
Changes in production affect total costs. Higher production volumes lower fixed costs per unit but may increase variable costs. The impact on profitability should be analyzed.
Want to put your knowledge to the test? Find a case partner or work on a case on your own – good luck! 🍀
Sample Case: Retirement homes
Prompt: A five-year-old company operating retirement homes in Germany recently opened a new home in Munich, but has profitability concerns. Analyze the cost structure:
- Fixed Costs
Examples: Rent, salaries, administrative costs.
Characteristics: Constant, independent of the number of residents. Must be covered even with low occupancy. - Variable Costs
Examples: Care costs, food.
Characteristics: Increase with the number of residents. Higher occupancy raises revenue and can improve profitability.
How to proceed?
- Break-even analysis: Determine the number of residents needed to cover fixed costs. Higher occupancy lowers costs per resident.
- Occupancy optimization: Strategies to increase occupancy in the new Munich home are essential to improve profitability.
- Cost reduction: Identify ways to reduce both fixed and variable costs to boost overall profitability.
In this case, a deep understanding of fixed and variable costs is vital to assess the senior care home’s profitability. Minimizing fixed costs and maximizing occupancy are key strategies for improving the financial situation and competitiveness.
Solve the full case here:
Key Takeaways
- Fixed and variable costs help analyze a company's cost structure and guide strategic decisions.
- In case interviews, they’re often used to assess a company’s profitability and identify cost-saving measures.
- Remember that each analysis should be tailored to the specific case. Understand the client’s needs and customize your approach.
With these tips and a clear understanding of fixed and variable costs, you're well-prepared to tackle challenges in case interviews. Don’t be discouraged – approach your cases with confidence! 💪
Interested in more essential calculations for case interviews? Explore articles on topics like opportunity costs, cost-benefit analysis and ROI and ROAS.