Porter's Five Forces is a powerful framework that helps companies and consultants assess the competitive landscape of a market. By analyzing five key factors - competition, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, buyer power and supplier power - you can determine the attractiveness of a market and its potential profitability. This tool is essential for anyone who wants to gain a strategic advantage when analyzing case studies in case interviews. Porter's five forces are especially relevant for market entry cases, since you need to assess the market attractiveness here.
Porter's Five Forces
Simplify Market Analysis with Porter’s Five Forces
A market is defined as a particular industry in which similar products are sold. Analyzing the competitive environment of a market can be quite difficult due to the numerous factors that need to be assessed. However, Porter's Five Forces Framework proves to be an effective tool for overcoming this complexity. This model evaluates five critical forces that determine the attractiveness of a market. In highly competitive markets, companies often have to invest significantly more resources to maintain their position, making these markets less attractive. The following schematic shows the elements of Porter's five forces:
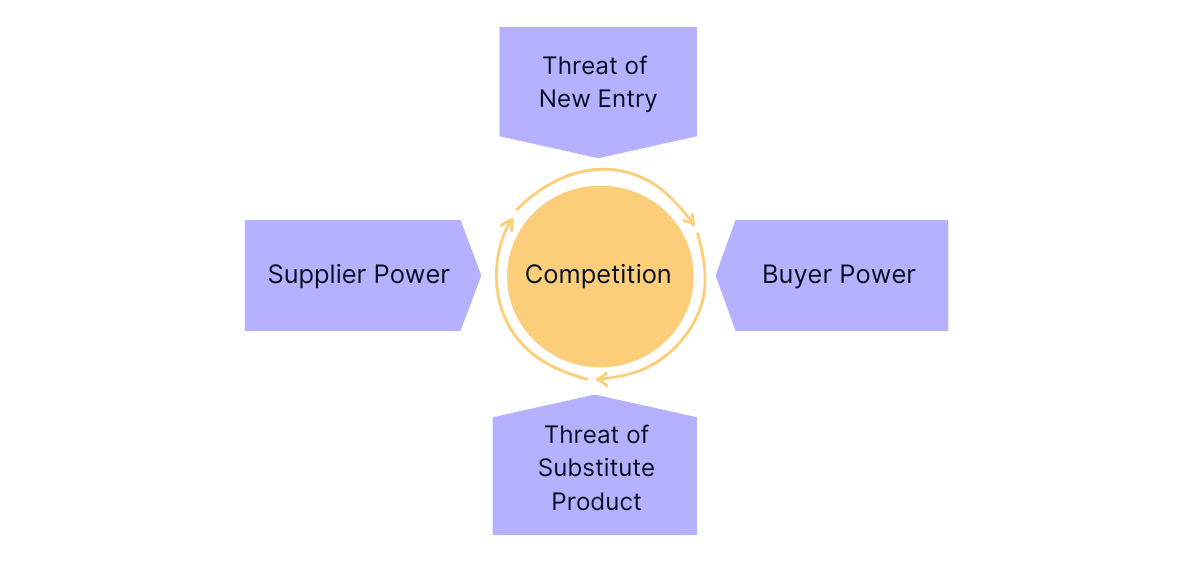
Analyze the Five Market Forces and Their Threats
When analyzing an industry, gather data on the five forces and evaluate their potential influence on the market. During a market analysis in a case interview, focus on asking targeted questions to effectively assess the strength of these forces.
Negotiating Power of Suppliers
The negotiating power of suppliers is defined as the amount of leverage the suppliers have for selling their products. A high negotiating power often leads to higher prices or lower quality, thereby lowering the potential margin of the industry.
Here are some indicators that a supplier wields significant negotiating power:
- Relatively lower threat for a supplier to get acquired by another company.
- High switching costs for a buyer to change suppliers.
- Availability of only a few suppliers (or high concentration of few suppliers).
- Highly specialized supplies, no substitutes for the supplied good.
Negotiating Power of Buyers
This concept is analogous to the supplier power discussed above. If buyers have a lot of negotiating power, it generally implies strong leverage to enforce low prices.
Here are some indicators that a buyer wields significant negotiating power:
- High danger of backwards integration or an ability of buyers to produce the product easily.
- Low switching costs.
- High concentration of customers or only a few customers relative to a number of suppliers.
- Large volumes of products bought by a single buyer.
- Better or easy alternatives for buyers to switch.
Threat from New Market Entrants
The lower the barriers for market entry, the easier it is for new competitors to enter the market thus leading to higher competition and thereby increasing the risk of price wars and a lower margin. Hence, an attractive industry usually has high entry barriers. It is hard to enter an attractive industry, but once a company is able to enter, it is in a good shape.
Market entry barriers:
- Economies of scale because new entrants sell lower volumes and face higher costs per unit.
- High learning effects because established players’ experience leads to better contracts, operations and customer relationships.
- High capital intensity and investment costs.
- Governmental regulations.
- Competitive environment.
- Low accessibility to suppliers and customers.
Threat of Substitute Products
Substitute products are alternatives to products that are obviously different but fulfill the same customer needs. The more substitute products, the easier it is for the customers to switch, thereby leading to a more competitive environment.
Following are a few indicators for a high threat of substitute products:
- Current products are old and at the end of the product life cycle.
- High comparability of replacement products and high visibility as a replacement.
- Similar prices.
Competition within the Industry
The level of industry rivalry is influenced by the remaining four forces of Porter, but is also subject to other causes. A high rivalry appears either as competition in terms of price or in terms of quality.
Signs of high rivalry:
- Very similar products.
- High number of market players competing against each other.
- Low or shrinking growth as competitors fight over a saturated market.
- High barriers of exit due to high sunk costs.
Using Porter's Five Forces in a Case Interview
Be cautious when applying Porter's Five Forces in a case interview. Interviewers may perceive the use of this framework as a last resort, indicating that you lack a more suitable structure for the solution. Ideally, you should integrate the Five Forces within a broader analytical framework (e.g., a cost-benefit analysis).This approach will demonstrate to the interviewer that you are not simply forcing the case into a specific model but are instead employing a well-considered and relevant methodology.
Key Takeaways to Remember About Porter's Five Forces
- Framework Overview: Porter's Five Forces evaluates industry attractiveness by analyzing competitive pressures: competition, the threat of new entrants, the impact of substitute products, and the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers.
- Industry Attractiveness: Strong forces typically reduce industry attractiveness and profitability. Porter's five forces are especially relevant for market entry cases.
- Integrated Approach: Combine Porter's Five Forces with other frameworks for a more comprehensive analysis in a case interview.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Perfect your skills by teaming up with case interview partners for regular practice sessions. Receive valuable feedback and sharpen your abilities together. Discover numerous case partners on our interactive Meeting Board!
You are looking for cases to practice Porter’s Five Forces with?
Check out our recommended resources or browse the Case Library for all cases on this topic.