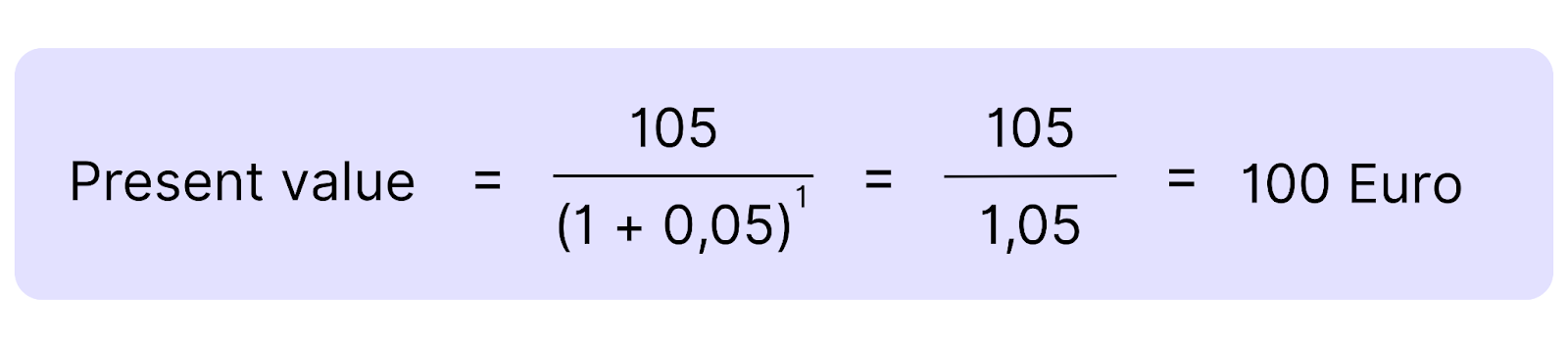Why Is the Present Value Important?
You’ll come across the Present Value in many situations, especially when dealing with money that comes (or goes) in the future. Here are some common examples where it’s useful:
- Comparing investments: You want to know if it makes sense to invest money today, even if the returns come later.
- Evaluating projects: Businesses use the Present Value to decide if a project will be financially worth it in the long run.
- Understanding loans and payment plans: The Present Value helps compare different loan offers or installment plans to see which one is really better.
- Calculating pensions or regular payments: If you’re getting monthly payments for several years, the Present Value helps you understand what the total is worth today.
How to Calculate the Present Value
The formula for the Present Value helps you “bring back” a future amount of money to today. Here’s how it looks like:
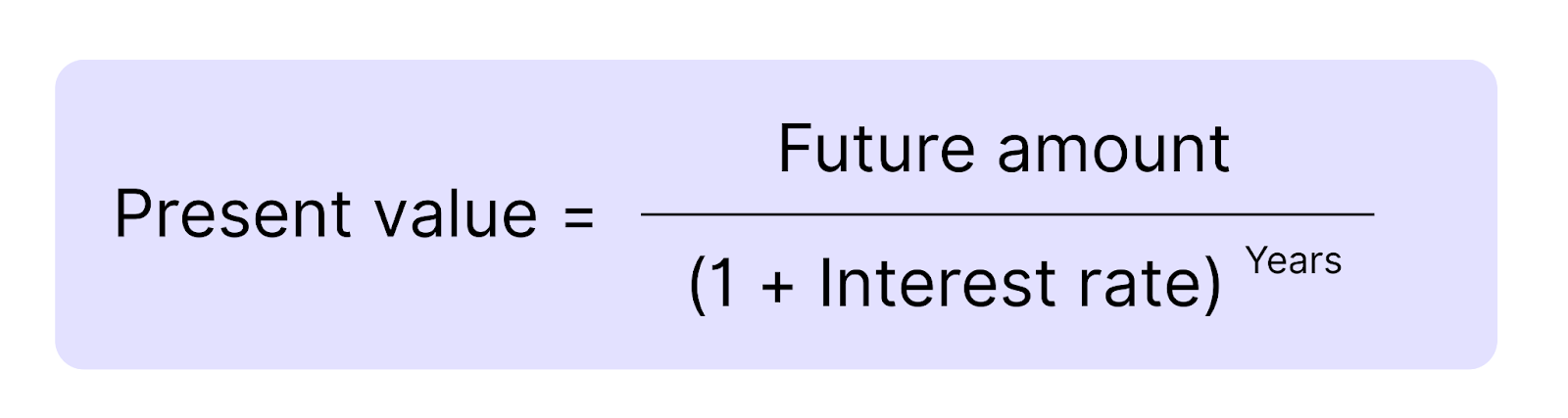
To calculate the Present Value, you divide the future amount of money by what’s called a discount factor.
This factor is made up of the interest rate and the number of years you have to wait for the money. With ‘(1 + interest rate)^years’, you basically bring the future amount back to the present. The higher the interest rate – or the longer the wait – the more the value is discounted, and the smaller the Present Value becomes.
Example: You’ll receive 105€ in one year at an interest rate of 5%. The Present Value of this money is calculated like this:
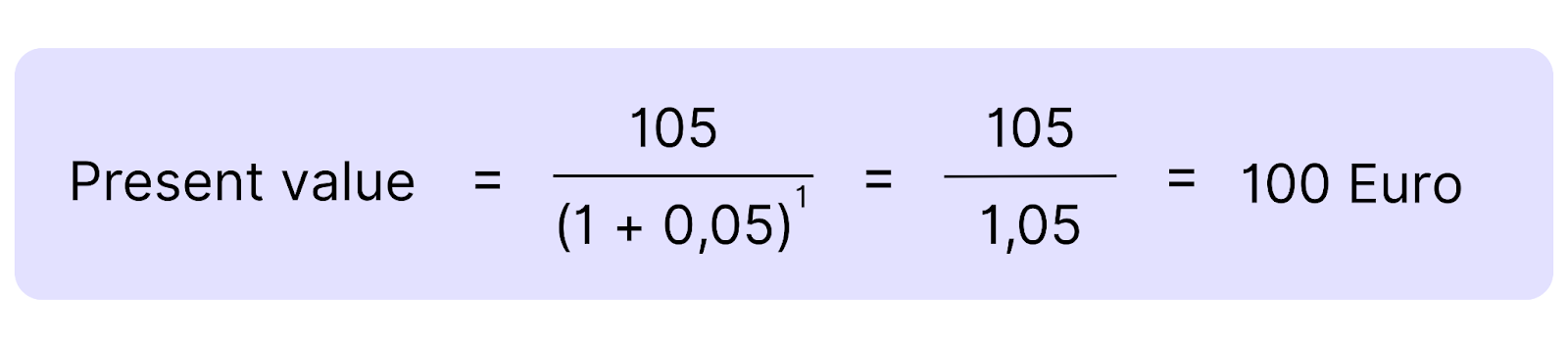
That means: 105€ in one year is worth 100€ today if you use a 5% interest rate.
Typical Questions About the Present Value in Finance Interviews
When you go into an interview, they won’t just ask if you know what Present Value is – they’ll want to see if you understand why it matters. Here are some typical questions and example answers to help you prepare:
What is the Present Value and why is it important?
The Present Value shows how much a sum of money that you’ll receive in the future is worth today. That’s important because money loses value over time – for example, due to inflation or because it could already be invested and earning interest today. This helps to better judge whether a project or investment is truly worth it.
What happens to the Present Value when the interest rate increases?
When the interest rate goes up, the Present Value goes down. That’s because I would need less money today to end up with the same amount in the future. So future money is worth less today if interest rates are higher.
What happens to the Present Value when the time period changes?
The further in the future the money is, the smaller the Present Value. That’s because I have to wait longer – and I miss out on potential interest for more years. So with each extra year, the value of future money becomes less today.
What’s the difference between Present Value and time value?
The time value of money is the general idea that money today is worth more than the same amount in the future. Present value is a specific calculation that tells me how much a future amount is worth today. You could say: Present Value makes the time value of money measurable and concrete.
👉 Find further questions you might encounter in a finance interview in our Case Library.