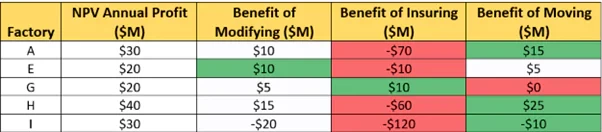
A mid-sized manufacturing company is concerned about the potential impacts of climate change on its operations. The company has a number of factories located in coastal regions that are vulnerable to flooding and other weather-related events, and it is concerned about the potential financial and reputational risks associated with these events. The company's leadership team has asked your consulting firm to help them understand the risks they face and develop a plan to mitigate those risks.
Clarifying Info:
- Our client’s objective is to maintain long-term profitability
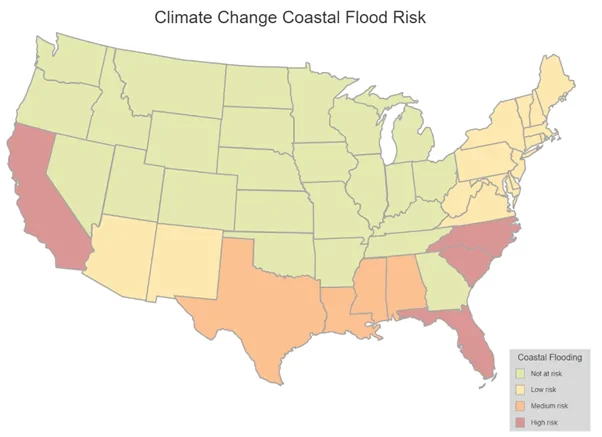
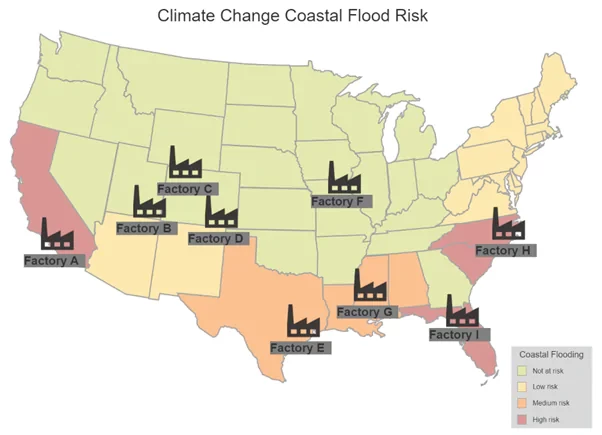
- Our client’s factories are located throughout the US
===================================================
Note: Once you have solved this case, make sure to solve the 2nd version of this case: MBB - Climate Change Operations - Part 2 | PrepLounge.com
This case is designed to show you how a case can evolve/change based on new information. The first half of this case is the same, but diverges once data and #s are provided.
To learn more about how to use case leadership to navigate dynamic cases, please read here: Candidate-Led Cases: What to Expect With Example Cases

MBB - Climate Change Operations
i