Hi everyone, I have one market sizing question that I encountered during my case interview months ago. Can anybody give me some feedback? BTW, I am still struggling with sanity check. What is the best way to do it? Thanks so much:)
Assess how many people work to deliver food in HK in 2021?
= The total number of ordered meals (total demand) / the number of meals one deliveryman can deliver
1. The number of meal one deliveryman can deliver
4h*(3meal*90%)=11
8h*(3meal*50%)=12
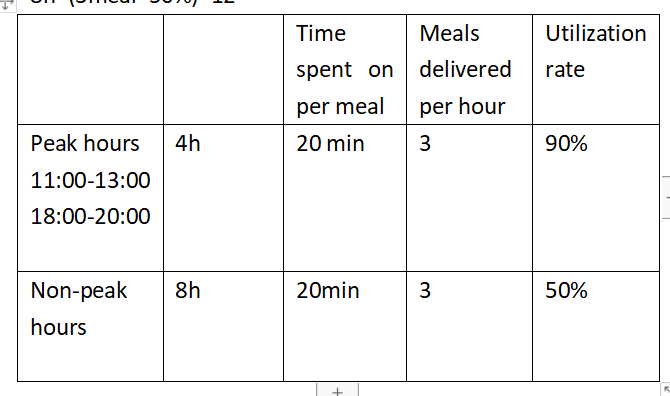
One deliveryman one day can deliver 11+12=23 meals
Assume that there are 360 days -> 23meals*360=8280meals/year
2. Total demand
HK population: 8million
8/4=2m
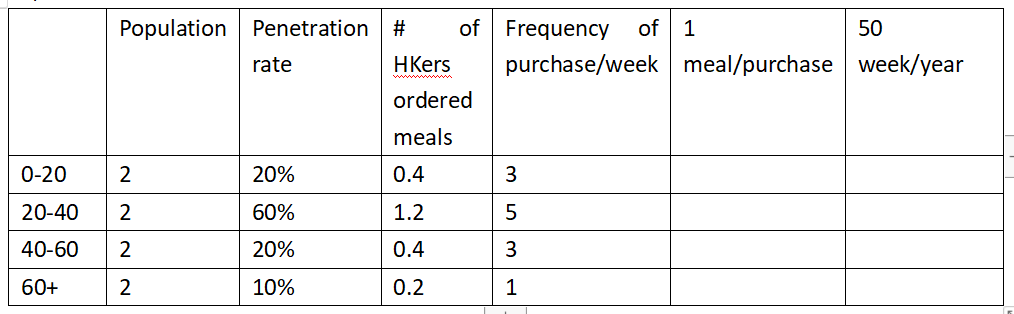
1.2+6+1.2+0.2=8.6m meals/week
8.6m*50=430m
430m/8280=52,000 delivermen










