Our client is NeuBank, a neobank in the US. A soccer stadium in Ohio is offering exclusive naming rights, and NeuBank is considering bidding for them. The client wants to understand the following:
- If this is a good idea?
- How much they should bid?
- How to make the deal a win-win?
NOTE that this case is very long and is meant for learning casing skills. If you intend to use it for mock practice then focus on very specific segments to complete it in time.
Also check out the video solution at the bottom of this page for a step-by-step work-along and detailed explanantion

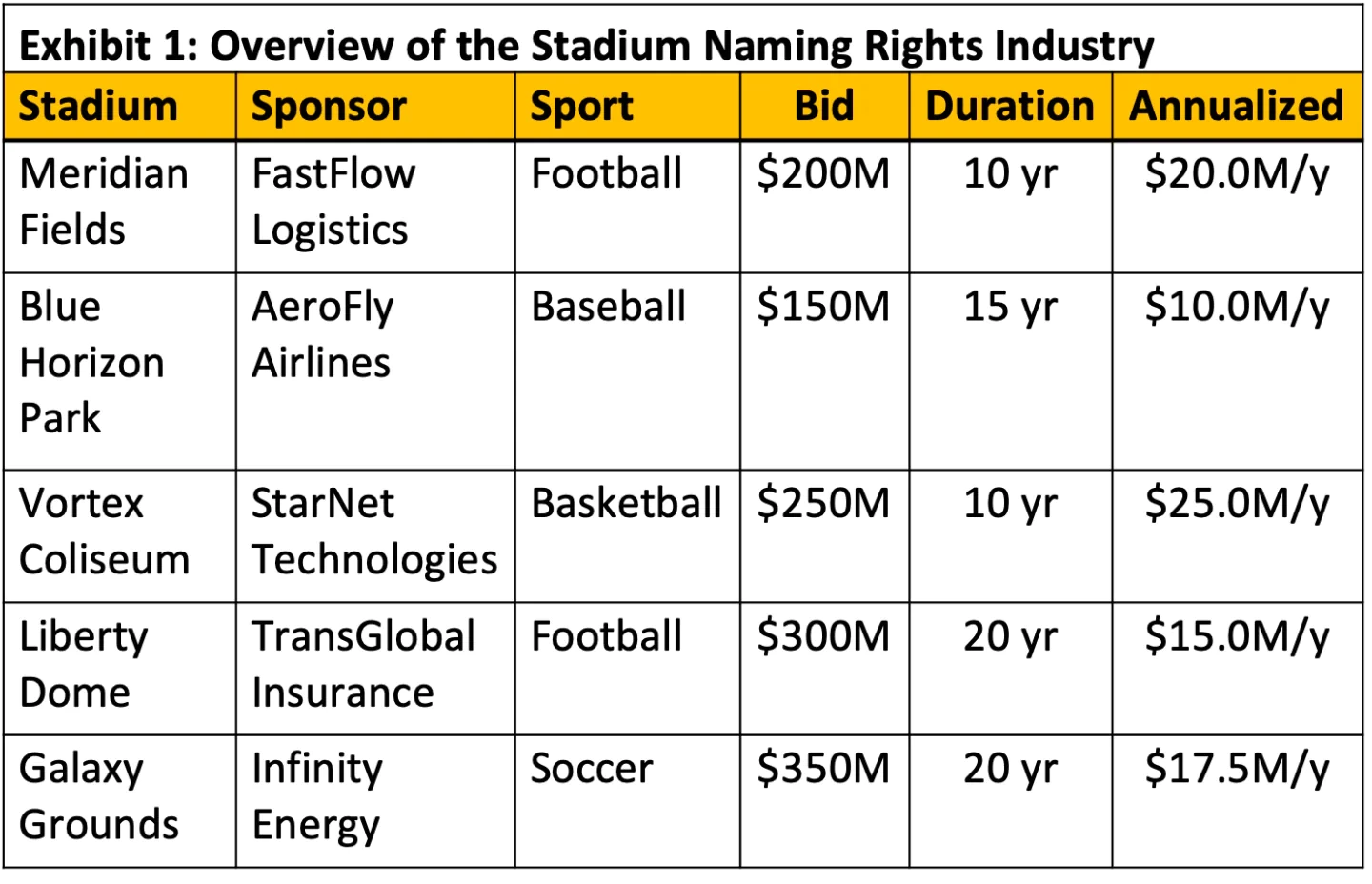
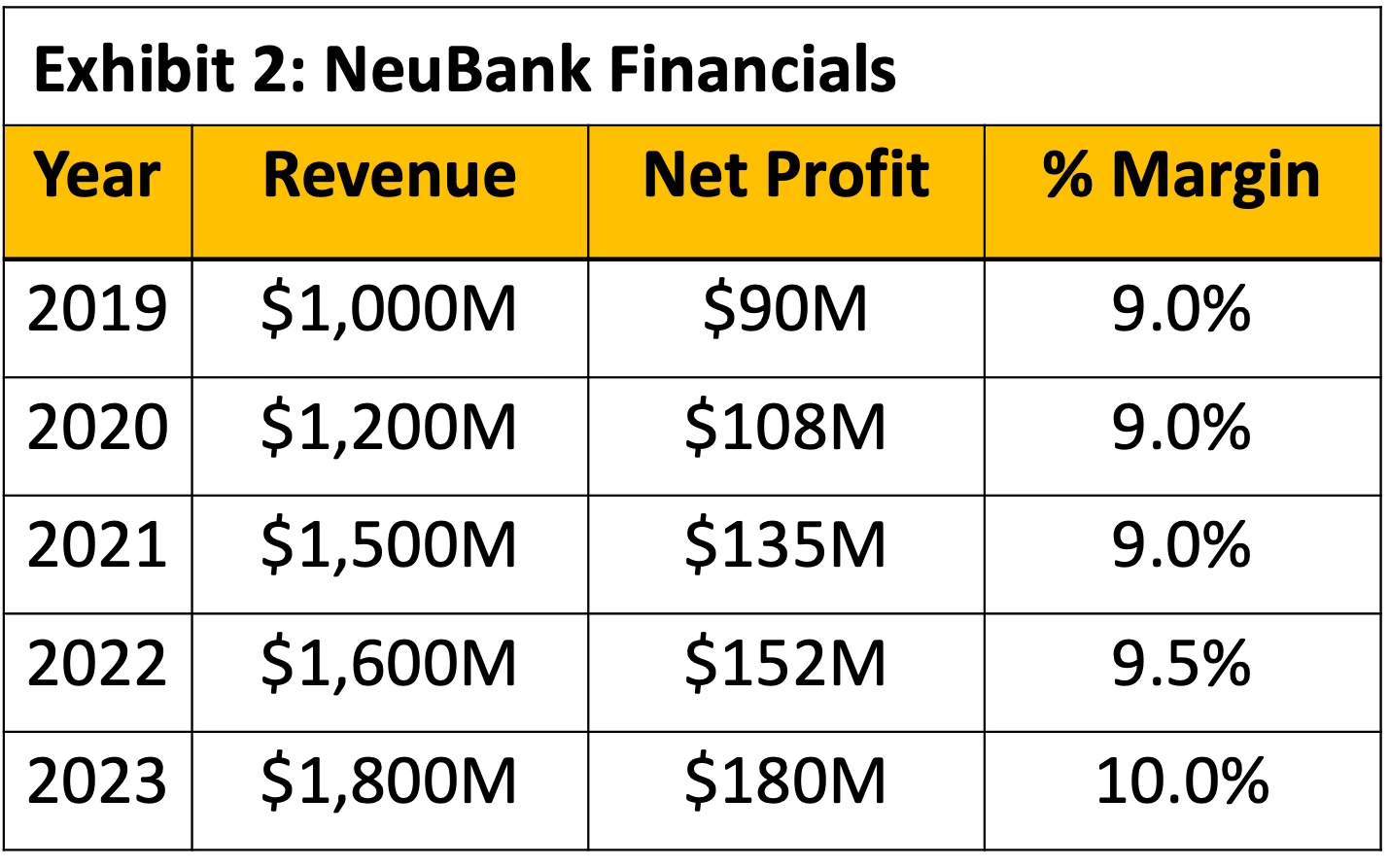
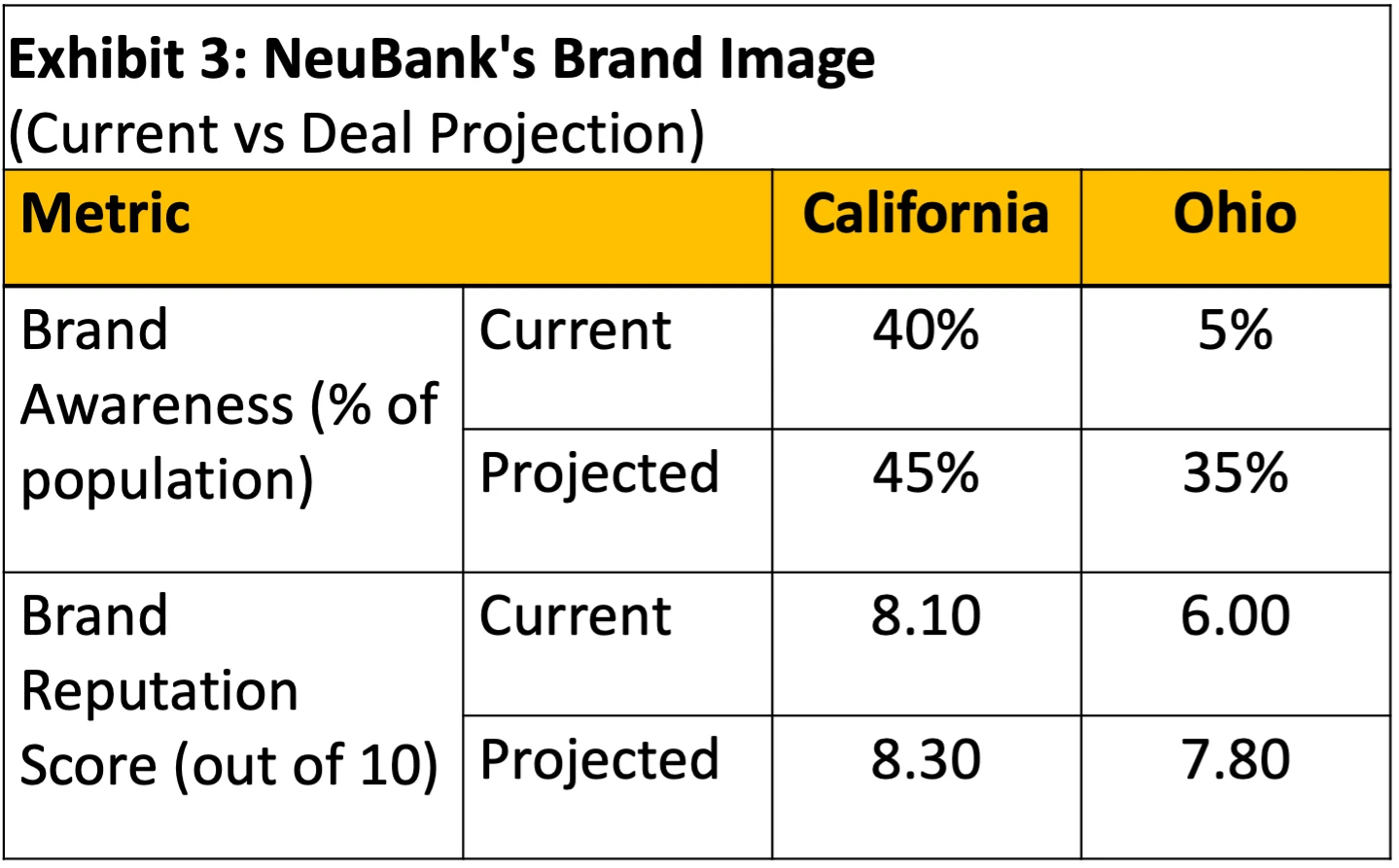
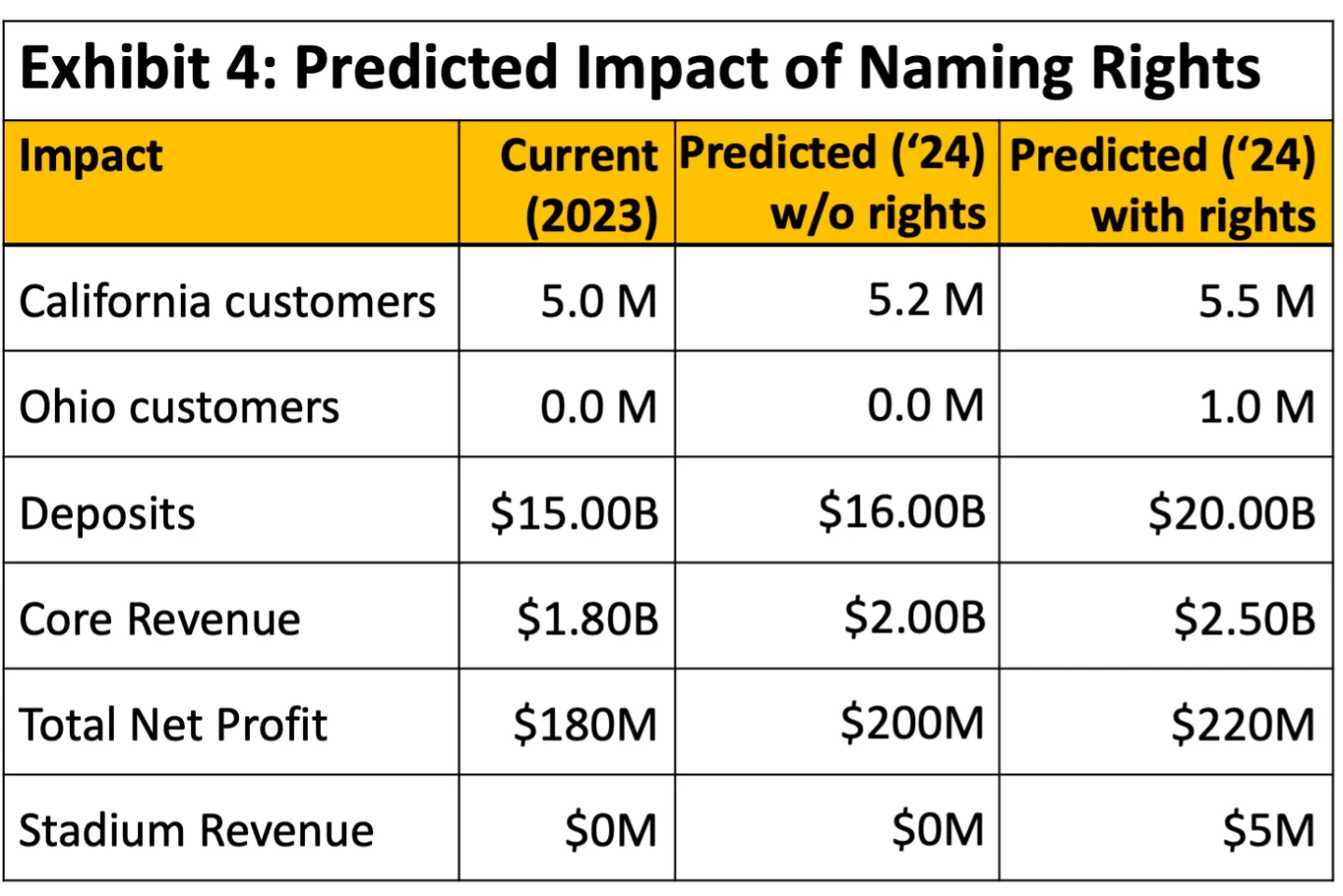

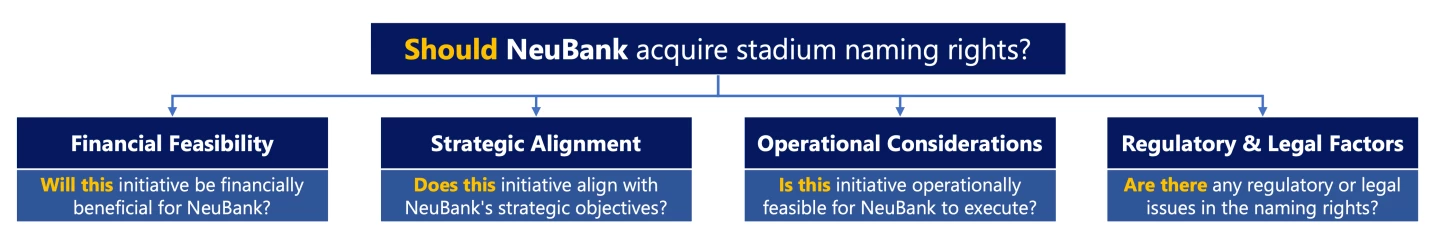
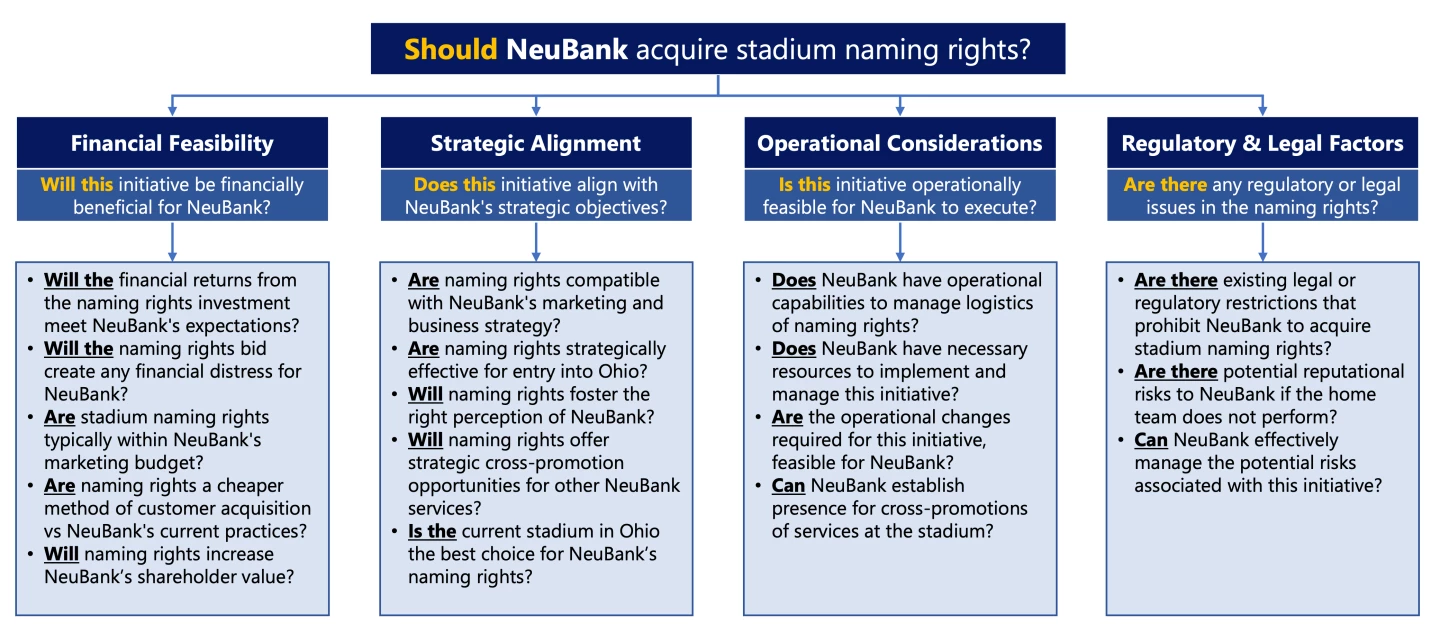

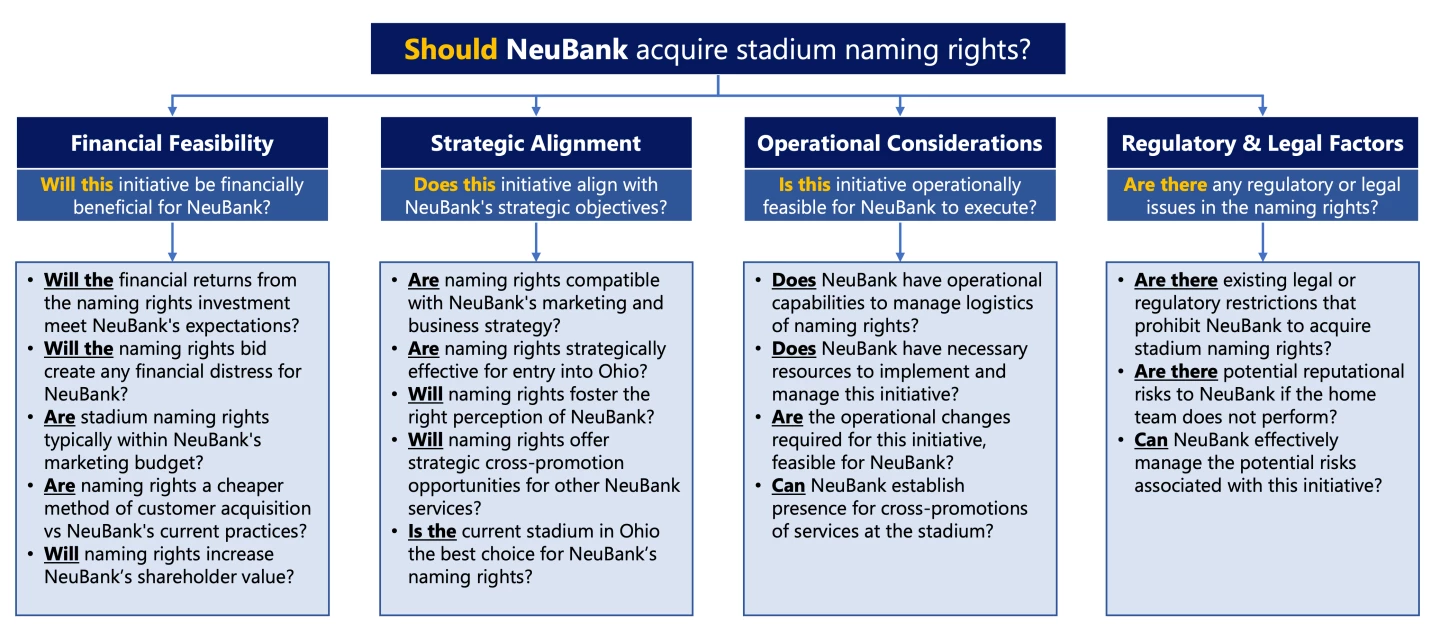

BCG Final Round: Stadium Naming Rights
i