Your client is the government of a region in southern Spain. Situated in this region are the country’s main tourist locations, mostly beaches.
The government is not satisfied with the revenues of the tourism sector. They have contacted our company to find a solution for this problem.
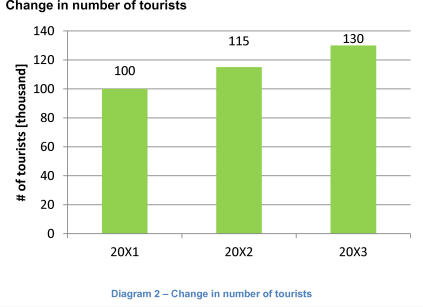
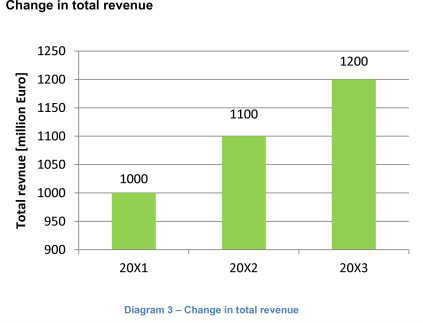
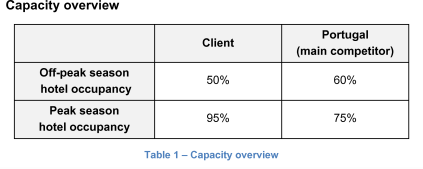

Travel Destination
i