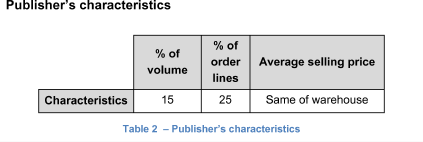
Your client, Bookl, is a publishing company with stable sales in terms of both volume and price.
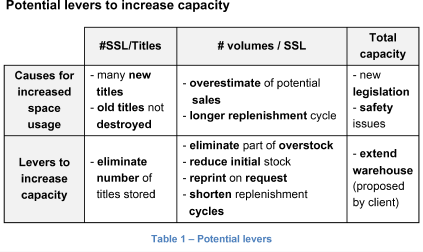
Its distribution warehouse is reaching maximum capacity. This has lowered its service quality.
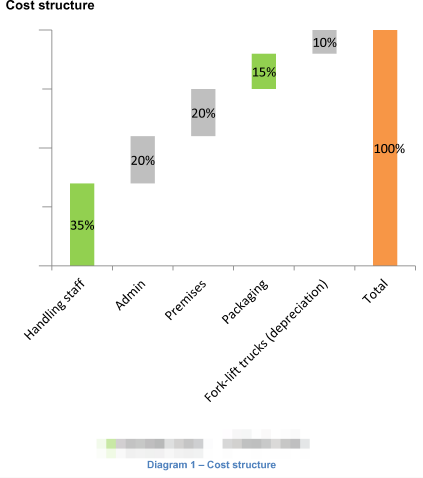
The head of Bookl’s distribution department wants to extend the warehouse. The extension will cost $15 m and will NOT increase the company’s revenues.
The CEO wants your company to determine whether the investment is necessary.


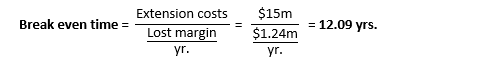

Bookl
i