Your client is an international Corporate & Investment Bank (CIB). It is France based and has already expanded to Poland (Warsaw), Asia and Americas. Your client now wants to look into the development of the existing hub in Warsaw and is contacting you to help him assess this option. How would you help him?
Case Prompt:
I. Savings
The cient already has a footprint in Warsaw which is only leveraged to nearshore French support functions.
a) What is the nearshoring potential in Warsaw ?
- Not all locations can be eligible for nearshoring out of the 4 client's locations.
- Some functions have higher potential than others.
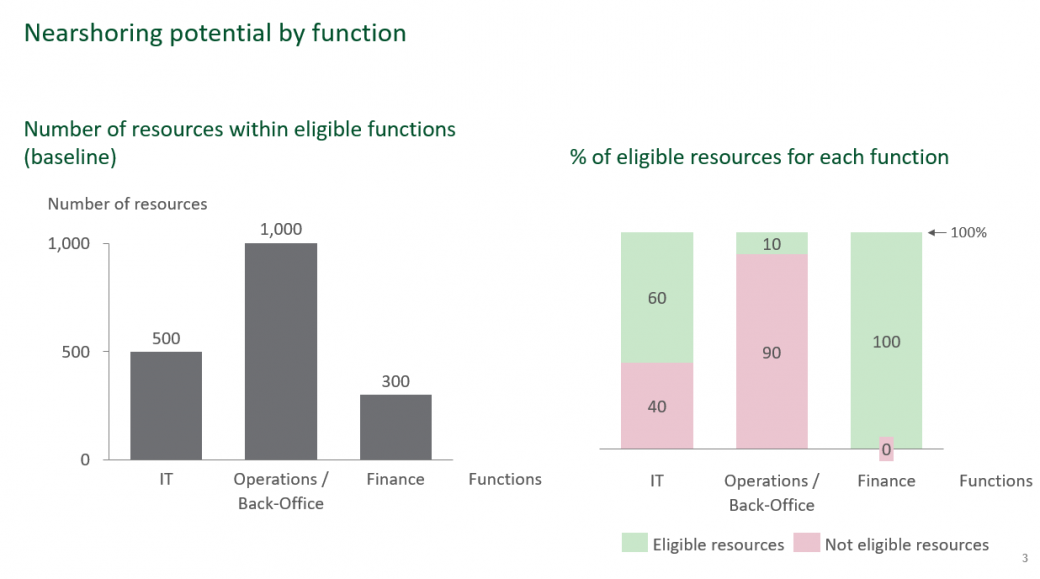
Share "Nearshoring potential by function" exhibit.

b) What could be the savings on the scope with nearshoring potential?
Salary (including all costs) is the main driver, thus, the level of salary in both Paris and Warsaw must be analyzed. Moreover, the environmental cost is the second element to be compared between Paris and Warsaw.
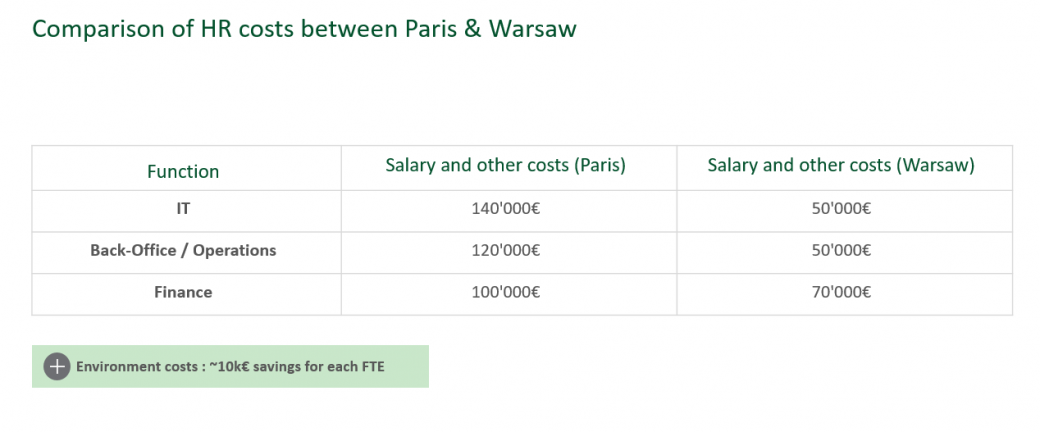
Share "Comparison of HR costs between Paris & Warsaw" exhibit.

a) What is the nearshoring potential in Warsaw?
- Warsaw is not relevant because it is the target nearshoring hub
- Nearshoring seems more difficult in Asia and Americas because of timezone and/or language constraints and thus higher operational risk and more difficulty to find relevant people in Poland (e.g. speaking Japanese)
- France seems to be the location with the highest potential, focus will be given on this country only
- Front Office is not eligible since Front Office representatives must have proximity with clients, out of eligibility scope
- Support functions seems to have higher potential; we can focus for example on IT, Operations (Back-Office) and Finance for instance.
- IT: 500 FTEs at stake // note : FTE means full time equivalent - number of full time resources in other words
- Operations / Back-Office : 1000 FTEs at stake
- Finance: 300 FTEs at stake
Out of all each eligible functions (total of eligible FTEs = 700 on the 3 perimeters), the volume of people eligible for nearshoring needs to be assessed.
- IT: 60% of FTEs are eligible for nearshoring (=300 FTEs)
- Operations / Back-Office: 10% of FTEs are eligible for nearshoring (=100 FTEs)
- Finance: 100% of FTEs are eligible for nearshoring (=300 FTEs)
b) What could be the savings on the scope with nearshoring potential?
- IT
- Averaged salary in Paris: 140k€
- Averaged salary in Warsaw: 50k€
- Back-Office / Operations
- Averaged salary in Paris: 120k€
- Averaged salary in Warsaw: 50k€
- Finance
- Averaged salary in Paris: 100k€
- Averaged salary in Warsaw: 70k€
Total salary savings is 43 millions €
- IT: 27 mn€
- Back-Office / operations: 7 mn€
- Finance: 9 mn€
On top of salaries, environment costs (participation in building costs, ...) must be compared (Paris vs. Warsaw).
- Averaged savings for each FTE is 10k€
- Savings due to different environment is 700 FTE x 10k€ = 7Mne
- Total savings is 43mn€ + 7mn€ = 50mn€
II. Implementation
a) What is the social impact?
- Not easy to lay off staff, especially in France, because of local labor jurisdictions and labor unions
- Voluntary departures will be preferred but will systematically encompass severance packages (= departure packages)
b) What are the implementation costs and what about ROI (Return on Investment)?
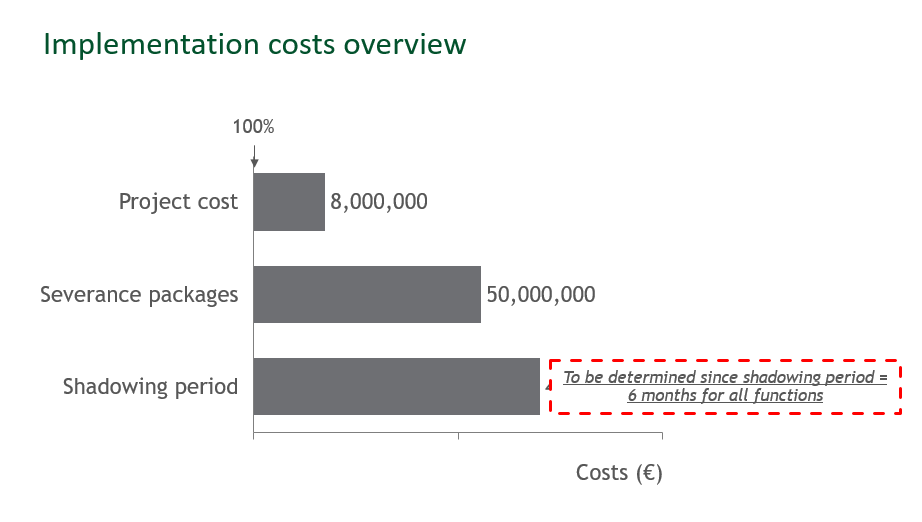
Share "Implementation costs overview" exhibit.

- As mentioned before, the amounts of severance packages must be determined: 50mn€
- To mitigate operational costs, Paris teams cannot be directly unplugged
- A shadowing period (transition period/time with both Paris & Warsaw teams) must be secured. This period will last 6 months.
- Since weighted average of salary is 120k€, the cost of shadowing period = 700 x 120k€ x 0,5 (Half-year only) = 42mn€
Finally, overall implementation costs, as well as ROI, could be computed levering all data provided so far.
- Overall costs for implementation = 50mn€ + 42mn€ + 8mn€ = 100mn€
- ROI can be positive from after 2.5 years
- Y1: Costs = 100mn€ and savings = 25mn€ (only 6 months)
- Y2: savings = 50mn€
- Y3: savings = 50mn€ (break even after 6 months of the third year)
Further Questions
1) Why do you think the Bank has a hub in Warsaw?
1) Why do you think the Bank has a hub in Warsaw?
The Bank has developed a hub in Warsaw for nearshoring purposed and thus to reduce operating costs
2) What are the most eligible functions for nearshoring in Porto?
2) What are the most eligible functions for nearshoring in Porto?
Front Office representatives need to be close to the clients. This highest potential will be on support functions.
3) Do you think that all locations of our client are eligible for nearshoring? What is the location with the highest potential (France, US, Apac)?
3) Do you think that all locations of our client are eligible for nearshoring? What is the location with the highest potential (France, US, Apac)?
There are a lot of feasibility constraints for the US & APAC (timezone, language). Thus, France is the best candidate for nearshoring out of the client's existing locations.
4) How to reduce operational risk implied by new staff being onboarded in Warsaw?
4) How to reduce operational risk implied by new staff being onboarded in Warsaw?
Keep onshore staff for 6 months (= shadowing period)
5) What could be the different costs implied by a nearshoring project?
5) What could be the different costs implied by a nearshoring project?
- Project costs
- Severance packages for leaving staff
- Shadowing period
6) What can we do instead of staff lay off?
6) What can we do instead of staff lay off?
- Voluntary departure

Nearshoring - Opportunity study and Business case
i