Your client is a direct mail clothing retailer. They primarily sell clothes through their product catalog. Next year, postage costs will increase to 40 cents per catalog. Your client wants to know whether his current business model is still profitable.
Case Prompt:
Sample Structure
The interviewee should calculate the profitability of the current business model under the new cost structure (it now costs 40 cents to mail one catalog).
Profit = Revenue – Costs
Suggested structure:
I. Revenue
Information that can be shared if inquired:
- The profit margin of orders is 15% (excluding mailing costs)
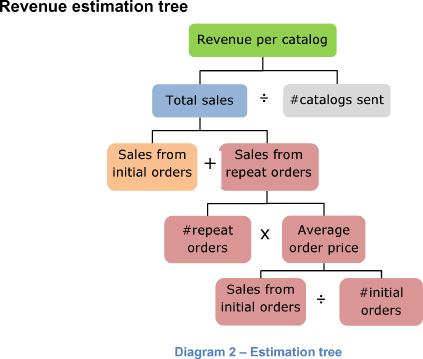
Share Diagram 2 with the revenue estimation tree.

Assumption:
The average repeat order price (some customers buy more than once from the retailer) is the same as the average price of the initial orders.
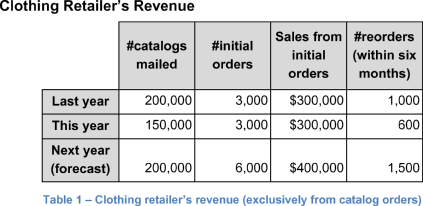
Share Table 1 with the revenue data of clothing retailer if inquired.

*Orders received within 2 weeks of sending the catalog are counted as initial orders.
First we need to calculate the revenue, because we have no information on the cost side.
The profit margin of orders is 15% (excluding mailing costs). Thus, excluding the mailing costs, the remaining costs are 85% of revenue. If the 40-cent mailing cost is greater than the 15% profit per order, the business is unprofitable.
Below is the structure of the revenue calculation:
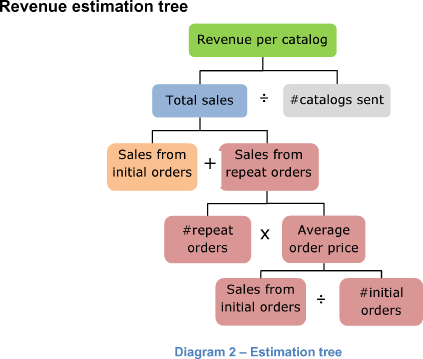
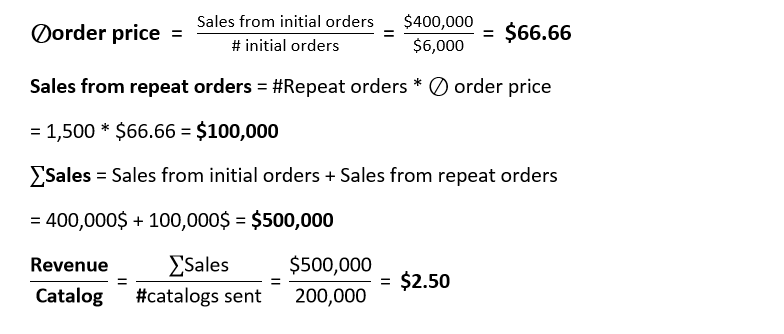
Once the structure is ready, we need to calculate the nodes of our tree. We will start from the leaves (nodes at the bottom of the tree) and use them to calculate higher-level nodes until we reach the top of the tree.
Main conclusion:
Each catalogue generates $2.50 in revenue.
II. Costs
On average, our client loses 2.5 cents for every catalog they send.

With the new 40-cent mailing cost, our client’s business model is now unprofitable.
III. Sustainability
The client wants to continue his clothing business. Ask the interviewee to suggest potential solutions.
Information that can be shared if inqiured:
- The retailer has a large variety of low-cost clothes. This is their unique selling point.
- Costs have been minimized over the entire value chain.
- The client operates in the European market. Orders via catalogs have decreased over the past few years. The client’s orders have also decreased.
- Price elasticity has been studied. Increasing prices will cause the number of customers to drastically decrease, thus decreasing revenue.
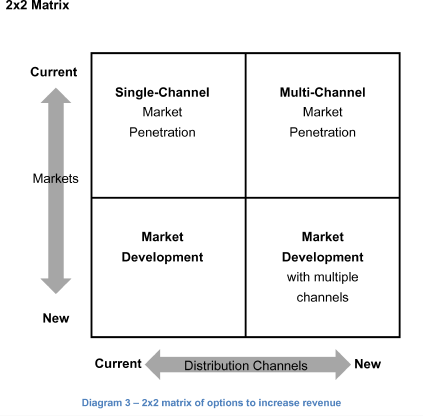
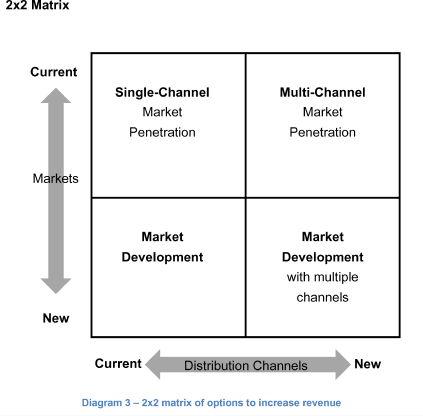
Share Diagram 3 (2x2 matrix) to guide the candidate towards this framework.

Challenge the interviewee and let him or her come up with as many channels and new markets as possible.
Since catalog orders in Europe seems like a declining industry, the interviewee could develop a 2x2 matrix with market and distribution channel as variables. It is similar to the Ansoff matrix. However, in this case, changing products makes little sense.
The interviewee can offer a variety of solutions.
Entering a new market
Lead the interviewee to a new market entry. It can be justified with the following reasoning:
- The current market is expected to shrink. A penetration strategy will be costly and unprofitable.
- Strong competitors are already using their European distribution channels.
- Emerging markets have an increasing number of people who can afford to buy cheap clothes.
Possible distribution channels
Possible reasons for using new distribution channels:
- In new markets, catalog orders are easily threatened by Internet orders. Currently, the company only uses the direct mail channel. They could launch an Internet site to receive orders.
- Due to market trends and market growth, obtaining market share online is a more sustainable move than attempting to maintain market share in Europe.
Since our client has a huge variety of low-cost clothes, they could become a wholesaler and sell clothes in bulk to smaller clothing retailers.
Further Questions
In order for the business to break even, by how much should the average order price increase?
In order for the business to break even, by how much should the average order price increase?
Suggested answer:
The revenue per catalog is proportional to the average order price. To break even, the business needs a per-catalog revenue of $2.525. That is a 1% increase from $2.5.
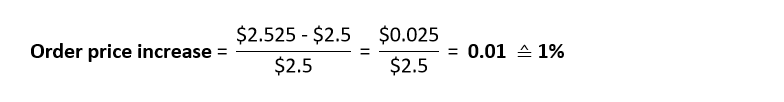
More questions to be added by you, interviewer!
If the interviewee solves the case very quickly, you can come up with more challenging questions to ask them.
More questions to be added by you, interviewer!
If the interviewee solves the case very quickly, you can come up with more challenging questions to ask them.




Fashion mail order
i